Fighting the Pregnancy Mask
Dealing with those stubborn dark patches during and after pregnancy? You’re not alone. Here’s your comprehensive guide to understanding and treating melasma safely and effectively.
What Is Melasma and Why Does Pregnancy Trigger It?
Melasma, often called the “pregnancy mask,” is a common skin condition characterized by symmetrical patches of hyperpigmentation that typically appear on the face. These brownish-gray patches commonly develop on the cheeks, forehead, bridge of the nose, upper lip, and chin.
During pregnancy, up to 70% of women may develop some form of melasma, typically during the second or third trimester. But why does pregnancy trigger these skin changes?
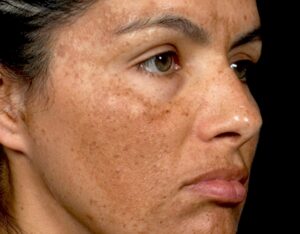
The Hormonal Connection
The primary culprit behind pregnancy-related melasma is the dramatic surge in hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone. These hormones stimulate melanocytes—the cells responsible for producing melanin (skin pigment)—causing them to go into overdrive.
Additionally, the placenta produces melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH), which further increases melanin production. This explains why melasma is sometimes called “the mask of pregnancy” or “chloasma.”
Other Contributing Factors During Pregnancy
While hormones are the main trigger, several other factors can worsen melasma during pregnancy:
- Sun exposure: UV radiation stimulates melanin production, intensifying existing melasma and triggering new patches
- Genetic predisposition: Family history plays a significant role in determining your susceptibility
- Skin tone: Those with darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III-VI) have more active melanocytes and are more prone to melasma
- Heat exposure: Often overlooked but critical—heat can stimulate melanocytes independently of UV radiation
Safe Melasma Treatments During Pregnancy
Managing melasma during pregnancy requires special consideration for both mother and baby’s safety. Here are safe, effective approaches to minimize pigmentation while pregnant:
Pregnancy-Safe Skincare Ingredients
When pregnant, focus on these gentle yet effective ingredients:
- Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant that brightens skin and inhibits melanin production. Look for stable forms like sodium ascorbyl phosphate or magnesium ascorbyl phosphate.
- Azelaic Acid: One of the few acids considered safe during pregnancy. It has anti-inflammatory properties and helps normalize melanin production.
- Niacinamide (Vitamin B3): Inhibits melanin transfer to skin cells and reduces inflammation. Studies show 4-5% concentrations can improve melasma.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, it inhibits tyrosinase (an enzyme involved in melanin production).
- Alpha Arbutin: A natural brightening agent that’s gentler than hydroquinone.
- Glycolic Acid (in low concentrations): When used in concentrations below 10%, this AHA can help with gentle exfoliation, improving the penetration of other active ingredients.
Pregnancy-Safe Skincare Routine
Morning Routine:
- Gentle cleanser
- Antioxidant serum (Vitamin C)
- Moisturizer with niacinamide
- Sunscreen (critical!) – More on this below
Evening Routine:
- Gentle cleanser
- Azelaic acid or alpha arbutin serum
- Rich moisturizer
- Optional: Low-concentration glycolic acid 1-2 times weekly
Sunscreen: The Most Important Thing You Can Do
Sunscreen is non-negotiable when managing melasma during pregnancy. Without proper sun protection, other treatments will be ineffective. Two excellent pregnancy-safe options include:
SkinBetter Science Sunbetter® SHEER SPF 70
- Mineral-based (zinc oxide and titanium dioxide)
- Provides physical barrier against UVA/UVB rays
- Free of chemical filters that could potentially disrupt hormones
- Elegant, sheer formula suitable for daily use
- Water-resistant formula perfect for active lifestyles
Colorescience Sunforgettable® Total Protection™ Face Shield SPF 50
- 100% mineral protection
- Contains additional antioxidants for added protection against free radicals
- Available in original and tinted versions to help even skin tone
- Brush-on powder format available for easy reapplication throughout the day
- Hypoallergenic and suitable for sensitive skin
Remember to reapply sunscreen every two hours when outdoors or after swimming/sweating.
Skincare Ingredients to Avoid During Pregnancy
While treating melasma, avoid these ingredients until after pregnancy and breastfeeding:
- Hydroquinone: The gold standard for hyperpigmentation treatment, but safety during pregnancy hasn’t been established
- Retinoids (retinol, tretinoin, adapalene, etc.): May cause birth defects
- High-concentration chemical exfoliants: Can increase skin sensitivity
- Salicylic acid (in high concentrations): While low concentrations in cleansers are generally considered safe, high-concentration products should be avoided
- Essential oils: Many have hormone-disrupting properties
- Oxybenzone and avobenzone: Chemical sunscreen filters with potential hormonal activity
Managing Melasma After Pregnancy
Once you’ve delivered your baby (and finished breastfeeding if applicable), you have additional options for treating persistent melasma. Postpartum treatment can incorporate more aggressive approaches:
Advanced Skincare Ingredients
After pregnancy, you can incorporate these powerful ingredients:
- Hydroquinone: The most effective topical agent for melasma, typically used in 2-4% concentrations for limited periods (8-12 weeks) followed by breaks
- Retinoids: Increase cell turnover and enhance penetration of other ingredients
- Tranexamic Acid: Emerging as a powerful treatment for melasma, available in both oral and topical forms
- Triple Combination Therapy: Often prescribed as “Kligman’s formula” containing hydroquinone, tretinoin, and a mild corticosteroid
- Cysteamine: A newer ingredient showing promise for melasma treatment. This ingredient can be found in Cyspera.
- Glutathione: Often used in combination therapies for its antioxidant and skin-brightening properties
Professional Treatments for Post-Pregnancy Melasma
Once your doctor gives clearance (typically 6 months post-delivery or after breastfeeding), these in-office treatments can dramatically improve stubborn melasma:
Laser Treatments
Halo Laser
- Hybrid fractional laser combining ablative and non-ablative wavelengths
- Targets both epidermal and dermal melasma
- Requires 3-5 days of downtime
- Generally requires 1-3 treatments spaced 4-6 weeks apart
- Results can last 1-2 years with proper maintenance
Moxi Laser
- Gentler fractional laser option
- Minimal downtime (24-48 hours of mild redness)
- Excellent for maintenance after more aggressive treatments
- May require 3-4 treatments for optimal results
- Can be combined with other treatments like BBL or chemical peels
Energy-Based Treatments
- Combines microneedling with radiofrequency energy
- Stimulates collagen while delivering heat to deeper skin layers
- Effective for dermal melasma that’s resistant to topical treatments
- Moderate downtime (3-5 days)
- Series of 3 treatments typically recommended
Chemical Peels
ViPeel
- Medium-depth peel containing TCA, retinoic acid, salicylic acid, phenol, and vitamin C
- Targets multiple layers of skin pigmentation
- 5-7 days of peeling expected
- Can be customized for melasma-specific concerns
- Series of 3-4 treatments recommended for optimal results
Cosmelan Peel
- Two-phase professional depigmentation system
- Phase one applied in-office, phase two continued at home
- Contains azelaic acid, kojic acid, phytic acid, and other brightening agents
- Specifically designed for melasma treatment
- Results visible within one week, with continued improvement over 30 days
- One of the most effective treatments for stubborn melasma
Combination Approach for Best Results
For optimal melasma improvement post-pregnancy, dermatologists typically recommend a multi-faceted approach:
- Professional in-office treatments (lasers or peels)
- Prescription-strength topicals for daily home use
- Strict sun protection and heat avoidance
- Anti-inflammatory diet rich in antioxidants
- Stress management to regulate hormones
Heat: An Overlooked Melasma Trigger
While most people know about sun protection, fewer understand that heat independently worsens melasma—even without UV exposure. This explains why melasma often flares in summer despite diligent sunscreen use.
How Heat Affects Melasma
Heat stimulates melanocytes through separate pathways from UV radiation. When skin temperature rises, it:
- Increases blood flow to the skin
- Triggers inflammatory responses
- Stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin
- Damages skin barriers, increasing susceptibility to environmental triggers
Common Heat Sources That Worsen Melasma
Be aware of these everyday heat exposures:
- Hot yoga and intense exercise that raise core body temperature
- Saunas and steam rooms
- Hot showers and baths
- Cooking over hot stoves without proper ventilation
- Hair dryers held close to the face
- Heated car interiors with direct sunlight
- Outdoor activities in warm weather
- Heated swimming pools
- Facial steamers used in skincare routines
- Hot beverages that raise facial skin temperature

Strategies to Keep Cool and Protect Your Skin
Try these practical approaches to minimize heat-induced melasma flares:
- Exercise in climate-controlled environments with good air conditioning
- Use cooling facial mists throughout the day (store in refrigerator for extra cooling)
- Apply ice rollers or cold compresses after heat exposure
- Switch to lukewarm water for face washing
- Try cooling masks with ingredients like aloe vera, cucumber, or chamomile
- Use portable fans when outdoors or cooking
- Choose early morning or evening for outdoor activities
- Wear cooling clothing with UV protection (UPF-rated fabrics)
- Stay hydrated to regulate body temperature
- Use cooling makeup primers with aloe or cucumber extracts
Preventing Melasma Recurrence
Melasma tends to recur, especially with hormone fluctuations, sun exposure, or seasonal changes. These long-term strategies will help maintain clear skin:
Daily Habits
- Reapply sunscreen every 2 hours when outdoors
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and seek shade
- Consider oral antioxidants like Polypodium leucotomos extract or Heliocare
- Keep skin cool with misting sprays
- Manage stress through meditation, adequate sleep, and exercise
- Consider hormone evaluation if melasma persists despite treatment
Seasonal Adjustments
- Increase antioxidant use during summer months
- Step up sunscreen SPF in high-UV seasons
- Consider maintenance laser treatments before summer
- Use more occlusive sunscreens during intense sun exposure
- Add physical barriers (hats, umbrellas) in peak sun seasons
Patience and Consistency Are Key
Melasma treatment—particularly during and after pregnancy—requires patience and consistency. With the right combination of professional treatments, home care, and preventive measures, you can significantly improve pregnancy-related melasma and reclaim your confidence. While complete elimination can be challenging, dramatic improvement is absolutely possible with the right approach.
You May Also Like: