The Best Treatment for Melasma: A Comprehensive Guide
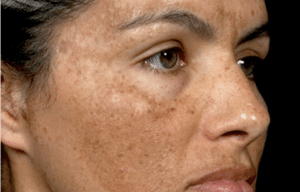
Melasma is one of the most challenging skin conditions to treat due to its chronic nature and the multitude of triggers that cause it to worsen. It commonly presents as brown or grayish patches on the face, including the cheeks, forehead, and around the mouth.
If you’ve noticed persistent dark patches and are asking yourself questions like, “Why is my forehead darker than my face?” or “How can I treat melasma around the mouth?”, you’re not alone. In this guide, we will explore the best treatment for melasma, including topical therapies and advanced procedures, as well as key tips for prevention and maintenance.
What Causes Melasma?
Melasma results from overproduction of melanin by melanocytes, the cells that create pigment in your skin. While hyperpigmentation can also be caused by inflammation or sun damage, melasma is usually triggered by hormonal changes, making it particularly common in women during pregnancy, while using birth control, or undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
Sun exposure is another major factor, as UV rays stimulate melanin production. Additionally, heat and visible light can worsen melasma, which means it can persist even with strict sun protection.
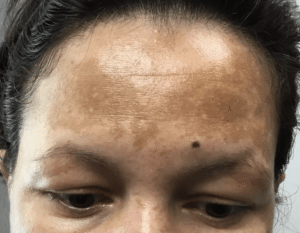
Why is My Forehead Darker Than My Face?
The forehead is often one of the first areas where melasma appears, especially when it’s more exposed to the sun. The skin here tends to be slightly thicker and more prone to increased melanocyte activity due to UV exposure, which can result in uneven skin tone. Hormonal fluctuations often exacerbate this, making the contrast between the forehead and the rest of the face even more noticeable.
Who Gets Melasma?
Melasma is more prevalent in people with darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick skin types III-V), particularly those of Hispanic, Asian, Middle Eastern, and Mediterranean descent. These skin types have more active melanocytes, which produce melanin more readily in response to triggers like sun exposure and hormonal changes. Women are disproportionately affected by melasma, with men accounting for only 10% of cases.
Factors That Worsen Melasma
Several factors can aggravate melasma or make it more resistant to treatment:
- Sun Exposure: Even minimal sun exposure can cause melasma to worsen, making broad-spectrum sunscreen an essential part of any treatment regimen.
- Heat and Infrared Light: Heat from the environment or even hot foods can cause the skin to become inflamed, which can worsen melasma.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Pregnancy, birth control pills, and hormone therapies significantly increase the risk of melasma.
- Inappropriate Treatments: Certain treatments that increase skin temperature, like IPL or lasers that aren’t designed for pigment, can make melasma worse by increasing inflammation.
How to Improve Melasma
Because melasma is a chronic condition, the first step in managing it is to avoid triggers and focus on treatments that prevent the formation of new pigment while gradually fading existing discoloration. Here are some general principles that should guide your treatment approach:
- Sun Protection is Key: Always use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 that protects against both UVA and UVB rays. For added protection, choose sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which physically block UV light.
- Consistent Skincare Routine: Incorporate products that contain retinoids, antioxidants, and pigment inhibitors to brighten the skin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Treatments with Long-Term Benefits: Melasma treatments should be ongoing, especially after summer months when UV exposure is more intense. Regular maintenance through both at-home products and in-office procedures is essential.
Topical Treatments for Melasma
Sunscreen
Sunscreen is the first line of defense against melasma. Opt for mineral-based formulas containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. These ingredients physically block UV rays and are less likely to irritate sensitive skin, unlike chemical sunscreens that can cause more heat absorption and exacerbate melasma. Daily sunscreen use should be a lifelong habit, and reapplication every two hours, especially if you’re outdoors, is crucial. Our favorite full coverage sunscreen is SkinBetter Science Tone Smart SPF 75.
Retinol for Melasma
Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives that accelerate cell turnover, helping to fade hyperpigmentation. Retinol, a milder form of retinoid, is often recommended because it’s more tolerable for sensitive skin, but stronger retinoids like tretinoin may be prescribed for more stubborn cases. Retinoids also stimulate collagen production, improving the overall texture and health of the skin. Because retinoids can make the skin more sensitive to the sun, they should be applied at night. One retinoid that is more tolerable without sacrificing effectiveness is SkinBetter Science AlphaRet Overnight Cream.
Antioxidants
Oxidative stress plays a significant role in worsening melasma, which is why antioxidants are a key part of treatment. Serums containing vitamin C can neutralize free radicals, prevent UV damage, and brighten the skin. Skinbetter Alto Defense Serum is a popular choice, combining 19 different antioxidants to protect the skin and reduce inflammation.
Specialty Products
- Cyspera (Cysteamine): Cyspera is a newer, non-hydroquinone treatment that effectively reduces melanin production. It’s a great long-term option for melasma, especially for patients who need to avoid the prolonged use of hydroquinone. The Cysteamine Isobionic-Amide Complex™ delivers 3 powerful effects for improved pigment correction and skin health.
- Cysteamine reduces melanin production in the melanogenesis pathway at multiple locations.
- Isobionic-Amide with AHA immediate reaction leads to instant pigment lightening in the corneal layer of the skin.
- AHA creates an acidic environment enhancing cysteamine permeability into the skin
- Skinbetter Even Tone Correcting Serum: This serum uses a combination of botanicals and peptides to brighten the skin without irritation. It’s suitable for long-term use, and ideal for patients with sensitive skin or those who want to avoid hydroquinone.
- Hydroquinone: Hydroquinone remains a gold standard in treating melasma. It works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme responsible for melanin production. However, it should only be used for three-month cycles, as prolonged use can cause irritation or even worsen hyperpigmentation due to a condition called ochronosis.
Cyspera vs. Skinbetter Even vs. Hydroquinone
- Cyspera is an excellent long-term solution and is well-tolerated for most skin types.
- Skinbetter Even offers a gentler approach with fewer side effects, making it ideal for sensitive skin.
- Hydroquinone is the most aggressive treatment but should be used cyclically to avoid long-term complications.
Advanced Treatments for Melasma
In addition to topical treatments, several in-office procedures can significantly improve melasma. These treatments should be performed by a trained professional who understands the intricacies of melasma, as improper treatment can lead to worsening pigmentation.
Chemical Peels
Chemical peels are an excellent option for melasma because they exfoliate the outer layers of the skin and promote cell turnover, reducing the appearance of pigmentation over time.
Cosmelan Peel: The Cosmelan Peel is a professional-grade depigmentation treatment that specifically targets melasma. It’s particularly effective because it inhibits tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production. The treatment consists of an initial in-office application followed by a home-care regimen. Results are usually visible within a few weeks, and it’s one of the most aggressive peels for stubborn melasma.
- Downtime of Cosmelan Peel: peeling and erythema 2-4 weeks
ViPeel: The ViPeel is a gentler chemical peel that combines trichloroacetic acid (TCA), salicylic acid, and vitamin C. It’s suitable for all skin types and helps improve the overall tone and texture of the skin while addressing pigmentation issues. The ViPeel is especially useful for those with sensitive skin who need a lighter exfoliation.
- Downtime of ViPeel: peeling up to 2 weeks
Microneedling
Microneedling is another excellent treatment for melasma because it stimulates collagen production and allows active ingredients to penetrate deeper into the skin. The process involves using tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries, which encourage the skin to repair itself, improving both texture and pigmentation. When microneedling is combined with topical treatments like tranexamic acid or antioxidants, the results can be significantly enhanced.
Microneedling with Tranexamic Acid: Tranexamic acid is an anti-pigmentation powerhouse that blocks pathways leading to melanin production. When applied during microneedling, it penetrates deeper into the skin, helping to break down stubborn pigmentation while preventing new melasma from forming.
- Downtime of Microneedling: mild redness and drying for 3-5 days
Tranexamic Acid Injections and Mesotherapy
Tranexamic acid can also be injected directly into areas of melasma to inhibit melanocyte activity. This treatment is particularly beneficial for those with hormonal melasma, as it addresses the root cause of hyperpigmentation at a deeper level.
- Downtime: Bruising can occur with injections which can last about 1 week
Mesotherapy, a treatment that delivers small amounts of active ingredients like tranexamic acid, vitamin C, or exosomes through microneedling devices like Aquagold, can further enhance results by delivering customized formulations directly into the skin. Exosomes (tiny extracellular vesicles) are particularly effective because they promote skin regeneration and help repair damage caused by UV exposure.
- Downtime of Mesotherapy: Mild redness for 1 day
Morpheus8 (RF Microneedling)
Morpheus8 combines microneedling with radiofrequency (RF) energy, delivering heat deep into the skin to tighten and remodel it. This treatment can improve melasma by boosting collagen production and reducing pigmentation over time.
Morpheus8 is especially beneficial for patients with melasma who also want to address issues like skin laxity and fine lines. The RF energy used in this treatment is controlled to prevent excessive heat that could worsen melasma, making it a safer option compared to other devices that use intense heat.
Moxie Laser
The Moxie laser is a non-ablative fractional laser that targets pigment while being gentle enough to treat sensitive conditions like melasma. It works by creating tiny controlled injuries to the skin, promoting the regeneration of healthy tissue without the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
What sets Moxie apart from other laser treatments is its ability to address pigmentation while also improving the overall texture of the skin. Since it doesn’t generate as much heat as other lasers, the risk of triggering more melasma is reduced.
PicoSure Laser
PicoSure is a non-thermal laser that targets pigment without causing heat damage to the surrounding tissue. It’s one of the safest laser treatments for melasma because it delivers energy in ultra-short pulses, reducing the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. The PicoSure laser is particularly effective at breaking up stubborn pigmentation, especially when combined with other treatments like microneedling or chemical peels. However, multiple sessions are often needed for optimal results.
Treatments to Avoid
While many treatments are effective in reducing melasma, some should be avoided due to the risk of worsening the condition:
- IPL (Intense Pulsed Light): IPL can cause increased inflammation, which worsens melasma, especially in darker skin types.
- Deep Lasers: Any laser that generates too much heat or aggressively targets deeper layers of the skin can trigger post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and make melasma worse.
Maintaining Results After Treatment
After achieving improvement in melasma, it’s essential to maintain your results with a consistent skincare routine and periodic professional treatments.
- Sunscreen: Continue daily sunscreen use, and reapply regularly.
- Topical Treatments: Incorporate antioxidants, retinoids, and pigment inhibitors like Cyspera or Skinbetter Even Tone into your skincare routine.
- Regular Treatments: Depending on your skin’s needs, you may need ongoing maintenance with microneedling, chemical peels, or lasers like Moxie or PicoSure.
Conclusion
Treating melasma is a multi-faceted approach that requires a combination of sun protection, topical treatments, and advanced in-office procedures. Whether you’re using topical retinoids, incorporating advanced laser treatments like Morpheus8, or exploring newer options like tranexamic acid injections, it’s important to remember that melasma is a chronic condition requiring consistent management. By working with a knowledgeable provider who understands the intricacies of your skin, you can achieve and maintain significant improvement.