Rare Brow Bone Reduction Complications: Double Vision
Brow bone reduction is a critical part of facial feminization surgery (FFS) which involves reshaping the forehead and orbital bones to soften the appearance of the brow ridge. While this surgery is typically safe, rare complications can arise, including double vision or diplopia.

A recent case report highlighted two instances of superior oblique palsy following FFS. Both patients experienced persistent double vision due to trauma to the trochlea, a small structure near the eye, during the reshaping of the orbital bones. One patient successfully managed the condition with prism spectacles, while the other required additional surgery to correct the issue.
What is Superior Oblique Palsy
Superior oblique palsy occurs when the superior oblique muscle, which is responsible for downward and inward eye movement, becomes weakened or paralyzed. This muscle works through the trochlea, a pulley-like structure in the upper orbit. Damage to the trochlear nerve (cranial nerve IV) or trauma can result in double vision (diplopia), particularly when looking down, and often leads to head tilting to compensate for the misalignment.
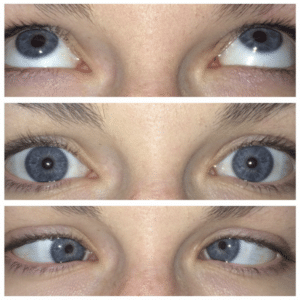
Treatment options include prism glasses, strabismus surgery, Botox injections, or observation, depending on the severity of the condition.
Why Brow Bone Reduction Can Cause Double Vision
Brow bone reduction often involves cutting and reshaping the bone near the frontal sinus. In aggressive techniques, particularly those using virtual surgical planning (VSP), the surgeon may need to elevate tissues surrounding the roof of the eye socket to access and contour the bones properly. This can lead to inadvertent damage to nearby structures, including the trochlea, which controls eye movement. If disturbed, patients can experience misalignment of the eyes, resulting in double vision.
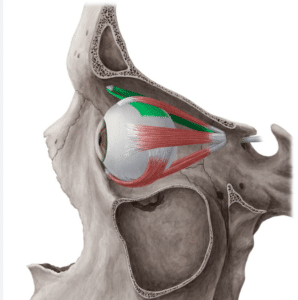
Below is a diagram of the superior oblique muscle (green) with it’s pulley insertion called the trochlea on the upper and inner surface of the eye socket.
Other Potential Complications of Brow Bone Reduction
While brow bone reduction complications are very rare, other potential complications can occur. These include bleeding, infection, hair loss, fluid collections under the skin, and nerve damage, leading to numbness or sensation changes in the forehead and scalp. More serious but rare complications include infections around the frontal sinus, mucocele, CSF leak or bone nonunion (incomplete healing of bone) can also occur.
Proper surgical technique and choosing an experienced surgeon can minimize these risks and ensure a smoother recovery.
The Importance of an Experienced Surgeon
To minimize the risk of complications like double vision, it’s essential to choose an experienced surgeon. Skilled surgeons are better equipped to handle the complexity of brow bone reduction and are more adept at balancing the aesthetic outcome with patient safety. By carefully planning the surgery and avoiding excessive tissue elevation, experienced surgeons, like Dr. Sarah Saxon, can reduce the likelihood of postoperative issues such as double vision.
While brow bone reduction is generally safe, these rare cases highlight the importance of careful technique to avoid complications. If you’re considering this procedure, selecting a qualified and experienced surgeon is key to achieving a successful and safe outcome.
In conclusion, while brow bone reduction complications are uncommon, they do occur, particularly when more aggressive techniques are employed in inexperienced hands.